The quality of a diamond is defined by means of the 4 Cs: carat, colour, clarity and cut. These four characteristics determine your stone’s value. And, as every diamond is unique, they are also very useful for identification.
CARAT
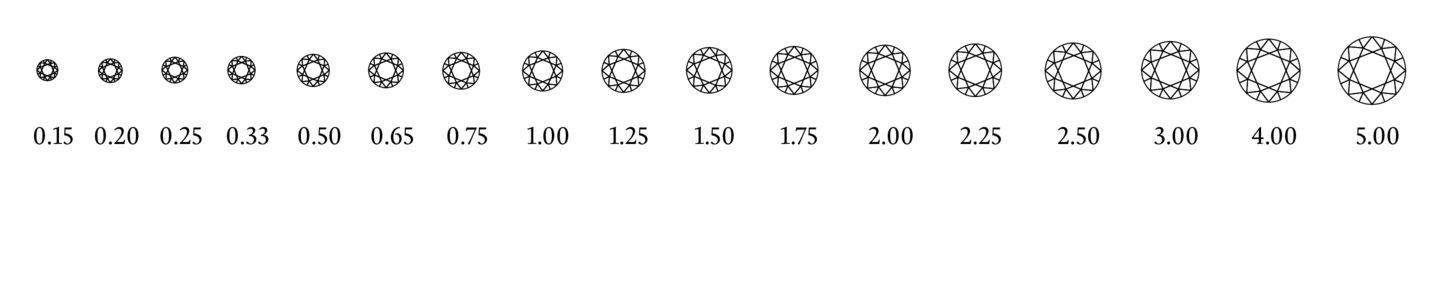 The weight of a diamond is expressed in carats. One carat equals 0.2 grams or 100 points. Each diamond is weighed immediately upon receipt at the reception desk. HRD in Antwerp has extremely accurate scales that measure up to 1/100,000 of a gram. This accurate weight is very useful for the identification of the diamond.
The weight of a diamond is expressed in carats. One carat equals 0.2 grams or 100 points. Each diamond is weighed immediately upon receipt at the reception desk. HRD in Antwerp has extremely accurate scales that measure up to 1/100,000 of a gram. This accurate weight is very useful for the identification of the diamond.
COLOUR
 Most diamonds range in colour from white to slightly yellow. However, diamonds can occur in all sorts of colours ranging from brownish to striking yellow, pink, purple, red and blue. These are called ‘fancy colours’.
Most diamonds range in colour from white to slightly yellow. However, diamonds can occur in all sorts of colours ranging from brownish to striking yellow, pink, purple, red and blue. These are called ‘fancy colours’.
CLARITY
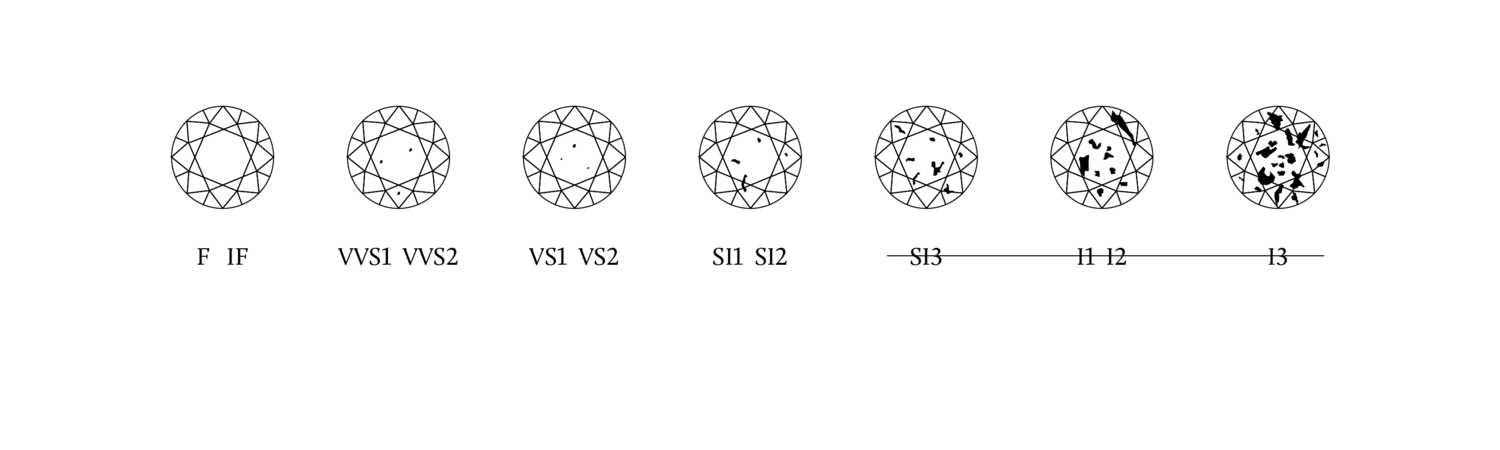 All diamonds have traces of their growth history. The clarity scale reflects the size, number, location and visibility of the internal characteristics when examined with a 10x loupe.
All diamonds have traces of their growth history. The clarity scale reflects the size, number, location and visibility of the internal characteristics when examined with a 10x loupe.
CUT
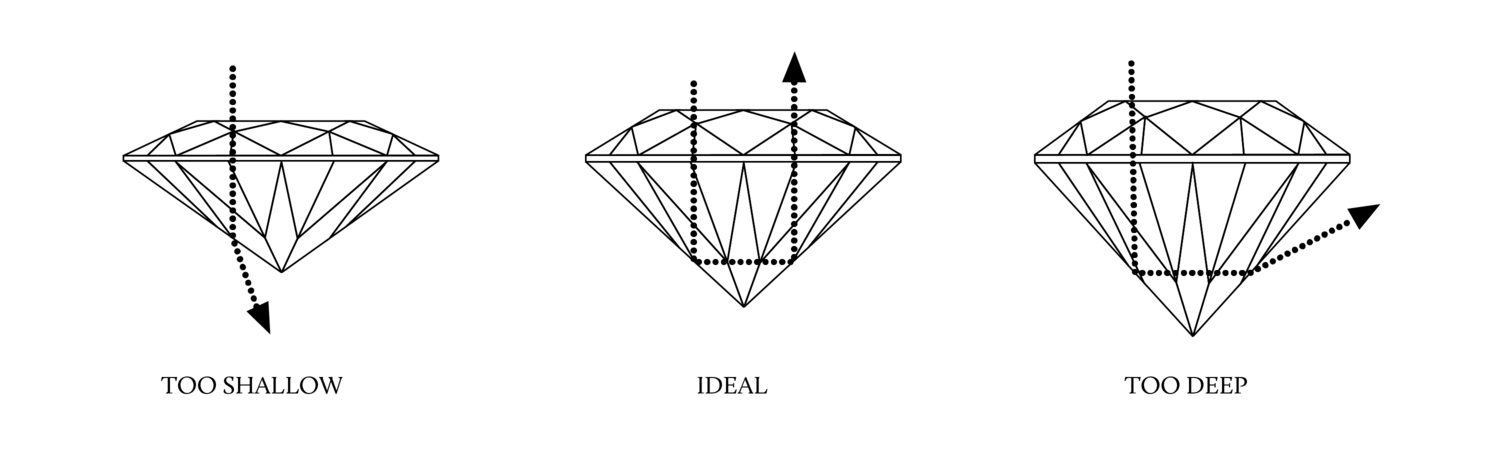
A diamond’s cut is essential to its beauty. If the diamond is not well-cut, the diamond will not interact with light as it should. Even a diamond with outstanding colour and clarity will not display the fire and brilliance that diamonds are famous for.
Since January 2009, HRD Antwerp has refined its cut grade, and now grades the diamond’s proportions, polish and symmetry. The polish describes the finish of the facets, while the proportions determine the brilliancy and the fire of the diamond. The symmetry describes the variations of the different parameters that define the proportions. Each grade is divided into 4 categories: Excellent, Very Good, Good and Fair.
SHAPE
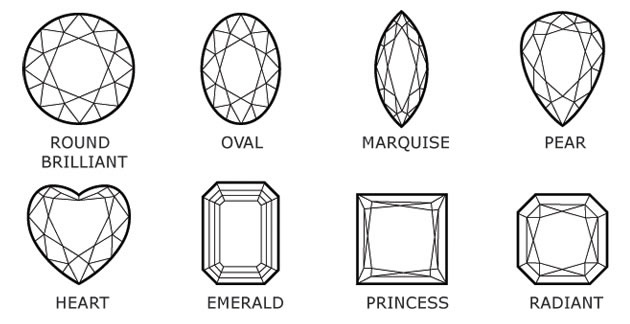
A common misunderstanding is that the term ‘diamond cut’ would also refer to the diamond’s shape. However, cut is what determines how well-cut your diamond is, whereas shape is the shape it was cut into. Diamonds can be cut into various shapes of which the round brilliant is probably the best known.
